instanceof 简介
在 JavaScript 中,判断一个变量的类型通常会用 typeof 运算符,在使用 typeof 运算符时采用引用类型存储值会出现一个问题,无论引用的是什么类型的对象,它都返回 “object”。例如:
|
|
如果想要确定原型和实例之间的关系就需要用到 instanceof 操作符, 例如:
|
|
Function instanceof Function ?
|
|
要解释这个问题就需要了解 1.JavaScript 语言规范中是如何定义 instanceof 运算符的,2.JavaScript 原型继承机制。
instanceof 运算符的定义
在 ECMAScript-262 中 instanceof 运算符的定义是这样的。
12.9.4 Runtime Semantics: InstanceofOperator(O, C)
The abstract operation InstanceofOperator(O, C) implements the generic algorithm for determining if an object O inherits from the inheritance path defined by constructor C. This abstract operation performs the following steps:1. If Type(C) is not Object, throw a TypeError exception. 2. Let instOfHandler be GetMethod(C,@@hasInstance). 3. ReturnIfAbrupt(instOfHandler). 4. If instOfHandler is not undefined, then a. Return ToBoolean(Call(instOfHandler, C, «O»)). 5. If IsCallable(C) is false, throw a TypeError exception. 6. Return OrdinaryHasInstance(C, O). NOTE Steps 5 and 6 provide compatibility with previous editions of ECMAScript that did not use a @@hasInstance method to define the instanceof operator semantics. If a function object does not define or inherit @@hasInstance it uses the default instanceof semantics.7.3.19 OrdinaryHasInstance (C, O)
The abstract operation OrdinaryHasInstance implements the default algorithm for determining if an object O inherits from the instance object inheritance path provided by constructor C. This abstract operation performs the following steps:1. If IsCallable(C) is false, return false. 2. If C has a [[BoundTargetFunction]] internal slot, then a. Let BC be the value of C’s [[BoundTargetFunction]] internal slot. b. Return InstanceofOperator(O,BC) (see 12.9.4). 3. If Type(O) is not Object, return false. 4. Let P be Get(C, "prototype"). 5. ReturnIfAbrupt(P). 6. If Type(P) is not Object, throw a TypeError exception. 7. Repeat a. Let O be `O.[[GetPrototypeOf]]()`. b. ReturnIfAbrupt(O). c. If O is null, return false. d. If SameValue(P, O) is true, return true.
官网的定义非常晦涩,上面的翻译成代码大概就是:
再直接点的表达就是 instanceof 会一直在 obj 的原型链上查找,直到找到右边那个构造函数的 prototype 属性,或者为 null 的时候才停止。
类似:
instanceof 会一直沿着隐式原型链 __proto__ 向上查找直到 obj.__proto__.__proto__ ...... === Obj.prototype 为止,如果找到则返回 true,也就是 obj 为 Obj 的一个实例。否则返回 false,obj 不是 Obj 的实例。
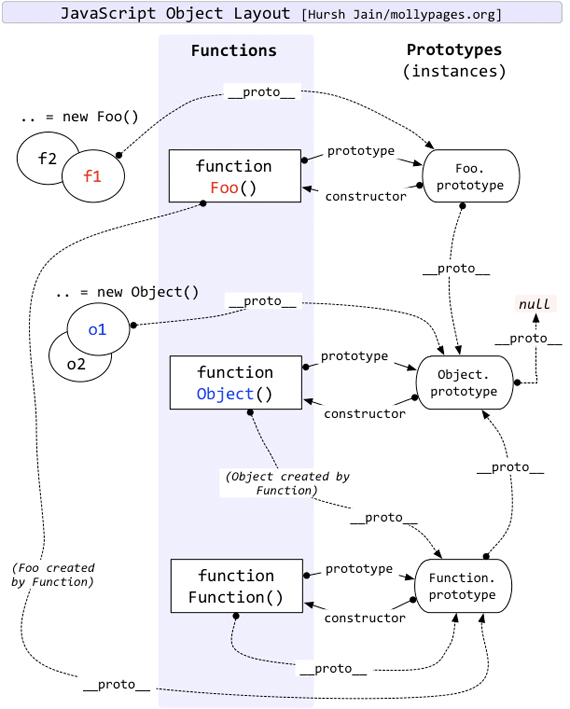
JavaScript 原型继承机制
原型与原型链
在 JavaScript 每个函数都有一个 prototype 属性,该属性存储的就是原型对象。JavaScript 构造函数的继承都是通过 prototype 属性, 真正的原型链的实现是通过 __proto__ 实现的,__proto__其实是指向‘父类’的 prototype 属性。例如:
原型继承
JavaScript 是单继承的,Object.prototype 是原型链的顶端,所有对象从它继承了包括 valueOf、toString 等等方法和属性。
Object 本身是构造函数,继承了 Function.prototype。 Function 也是对象,继承了 Object.prototype。
Object instanceof Object
|
|
String instanceof String
|
|
一切皆对象?
常常说 JavaScript 中一切皆对象,那么就有这样一个问题了:
|
|
按照上面的推导,'string' instanceof String 应该为 true,但是我们得到的却是 false。
其实问题的关键在于:
‘string’ 并不是一个 object 对象,MDN 上对 instanceof 的定义是:
The instanceof operator tests whether an object in its prototype chain has the prototype property of a constructor.
这样又有一个问题了,既然字符串不是对象那为什么有对象才有的属性和方法呢?
|
|
为了便于操作基本类型值,ECMAScript 还提供了 3 个特殊的引用类型: Boolean、Number 和 String。 实际上,每当读取一个基本类型值的时候,后台就会创建一个对应的基本包装类型的对象,从而让我们 能够调用一些方法来操作这些数据。
《JavaScript高级程序设计》中是这么解释的:
上面的例子其实当第二行代码访问 s1 时,访问过程处于一种读取模式,也就是要 从内存中读取这个字符串的值。而在读取模式中访问字符串时,后台都会自动完成:
(1) 创建 String 类型的一个实例;
(2) 在实例上调用指定的方法;
(3) 销毁这个实例。
可以将以上三个步骤想象成是执行了下列 ECMAScript 代码。
《Javascript权威指南》里说:
其实(包装对象)在实现上并不一定创建或销毁这个临时对象,然而整个过程看起来是这样的。
这样 Boolean、Number 是一样的逻辑。还剩下两种基本类型:null 和 undefined。
undefined 当我们对变量只声明没有初始化时,输出为 undefined,typeof undefined 返回的是 undefined 也不是 object 类型,所以 undefined 并不是任何对象的实例。
null 表示的是空对象,虽然 typeof null 是 object,但是 null 和 undefined 一样并没有任何属性和方法,在 instanceof 定义中也有判断,如果类型不是 object(这个类型判断并不是跟 typeof 返回值一样),就返回 false。